|
Size: 4044
Comment:
|
Size: 4812
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| This page documents the implementation of external functions in Dynare 4. We call ''external functions'' those functions that are not part of the small set of functions natively supported by Dynare (e.g., log, exp, etc). | This page documents the implementation of external functions in Dynare 4. We call ''external functions'' those functions that are not part of the small set of functions natively supported by Dynare (e.g., log, exp, etc). Essentially, this feature allows Dynare 4 to operate on any user-defined (or built-in Matlab) function. For the remainder of this wiki, we assume that the user wants to use a function called {{{funcname}}} in her model. |
| Line 3: | Line 3: |
| Essentially, this feature allows Dynare 4 to operate on any user-defined (or built-in Matlab) function. = User Syntax = We assume that the user wants to use a function called {{{funcname}}} in his model. The function is supposed to be implemented through a M-file or a MEX file, located in MATLAB path (this definition includes built-in MATLAB functions). |
= The External Function = The function can be implemented through a M-file or a MEX file (hereafter, M-/MEX file) located on the MATLAB path. '''NB:''' This includes built-in MATLAB functions. |
| Line 11: | Line 8: |
| The user has three options with regards to providing the derivative of the function to Dynare: 1. Provide no derivative. In this case, Dynare will calculate the numerical derivatives using finite differences; 1. Provide the first (and possibly second) derivatives in the same M-file as the function itself. The first derivative will be the second return argument (the Jacobian, in a vector) and the second derivative will be the third return argument (the Hessian, in a matrix). 1. Provide the first (and possibly second) derivatives in separate M-files. In this case, the only return argument to these functions will be a vector in the case of the Jacobian and a matrix in the case of the Hessian. |
There are two ways in which the user can provide the derivative of {{{funcname}}} to Dynare: |
| Line 16: | Line 10: |
| The keyword {{{external_function}}} will be used for the declaration of external functions. It accepts the following options: * {{{name = STRING}}}: the name of the function, which must also be the name of the M-file (or MEX file) implementing it * {{{nargs = INTEGER}}}: the number of arguments of the function. Defaults to 1 * {{{first_deriv_provided}}}: tells Dynare that the M-file also returns the first derivatives, as the second output * {{{first_deriv_provided = STRING}}}: tells Dynare that the first derivatives of the function are provided by the M-file given as option argument * {{{second_deriv_provided}}}: tells Dynare that the M-file also returns the second derivatives, as the second output * {{{second_deriv_provided = STRING}}}: tells Dynare that the second derivatives of the function are provided by the M-file given as option argument |
1. '''Provide the first (and possibly second) derivatives in the same M-/MEX file as the function itself:''' The first derivative will be the second return argument (the Jacobian, in a vector) and the second derivative will be the third return argument (the Hessian, in a matrix). 1. '''Provide the first (and possibly second) derivatives in separate M-/MEX files:''' In this case, the only return argument to these functions will be a vector in the case of the Jacobian and a matrix in the case of the Hessian. |
| Line 24: | Line 13: |
| This keyword would be used in the first part of the MOD file (where variable declarations are), possibly several times if several external functions are used. | '''Further, the user has the option to provide neither the first nor the second derivative of {{{funcname}}}.''' In this case (and in the case when the first derivative is provided but the second is not), Dynare will calculate the missing derivatives numerically using finite differences methods (central differences for the Jacobian and eqs. 25.3.24 and 25.3.27 from [[http://mintaka.sdsu.edu/faculty/wfw/ABRAMOWITZ-STEGUN/page_884.htm|Abramowitz and Stegun (1965), pg 884]] for the Hessian); |
| Line 26: | Line 15: |
| Since external functions are already accepted outside the MOD file without any specific declaration, we should keep the following convention: if during the parsing (inside or outside the model block), the parser encounters an unknown function name, then it should behave as if a external function declaration had been made for that function, with the number of arguments used in the construct, and without any provided derivative. Put otherwise, if the parser encounters something like {{{funcname(x, y, z)}}} and there is no explicit external function declaration, then it should generate an implicit external function declaration like the following: | === Example === 1. The case when one M-/MEX file contains the function output, its Jacobian and Hessian: |
| Line 28: | Line 18: |
| external_function(name = funcname, nargs = 3); | function [y df d2f]=funcname(a,b) y=a*(b^2); da=b^2; db=2*a*b; df=[da db]; d2f=[0 2*b; 2*b 2*a]; end |
| Line 31: | Line 29: |
| == Syntax examples == | 2. The case when there is a separate M-/MEX file for {{{funcname}}} and its derivative, {{{funcname_deriv}}}: {{{ function y=funcname(a,b) y=a*(b^2); end |
| Line 33: | Line 35: |
| * Declare an external function with name {{{funcname}}}, accepting only one argument, and whose derivatives must be computed numerically by Dynare: | function df=funcname_deriv(a,b) da=b^2; db=2*a*b; df=[da db]; end }}} = User Syntax in the .mod file = The keyword {{{external_function}}} is reserved for the declaration of external functions. It accepts the following options: * {{{name = STRING}}}: the name of the function, which must also be the name of the M-/MEX file implementing it. * {{{nargs = INTEGER}}}: the number of arguments of the function. If this option is not provided, Dynare assumes {{{nargs = 1}}}. * {{{first_deriv_provided}}}: tells Dynare that the M-/MEX file specified by the argument passed to {{{name}}} returns the Jacobian as its second output argument. * {{{first_deriv_provided = STRING}}}: tells Dynare that the Jacobian is provided as the only output of the M-/MEX file given as the option argument. * {{{second_deriv_provided}}}: tells Dynare that the M-/MEX file specified by the argument passed to {{{name}}} returns the Hessian as its third output argument. * {{{second_deriv_provided = STRING}}}: tells Dynare that the Hessian is provided as the only output of the M-/MEX file given as the option argument. The {{{external_function}}} keyword should be used in the first part of the MOD file where the variable declarations are. It should be used once for every external function used. The user does not need to include an {{{external_function}}} statement if no first or second derivative is provided. In this case, the Dynare preprocessor will recognize the external function (and the number of arguments that have been passed to it) and calculate numerical derivatives as described above. === Examples === 1. Declare an external function with name {{{funcname}}}, accepting only one argument, whose derivatives must be computed numerically by Dynare: |
| Line 37: | Line 62: |
| * Declare an external function with two arguments, whose derivatives are returned as second and third output argument of the implementation: | 2. Declare an external function with name {{{funcname}}}, accepting two arguments, whose derivatives are returned as the second and third output arguments of the M-/MEX file {{{funcname}}}: |
| Line 41: | Line 66: |
| * Declare an external function with three arguments, whose first derivative is provided by M-file funcname_deriv, and whose second derivative must be computed numerically by Dynare: | 3. Declare an external function with three arguments, whose first derivative is provided by the M-/MEX file {{{funcname_deriv}}}, and whose second derivative must be computed numerically by Dynare: |
This page documents the implementation of external functions in Dynare 4. We call external functions those functions that are not part of the small set of functions natively supported by Dynare (e.g., log, exp, etc). Essentially, this feature allows Dynare 4 to operate on any user-defined (or built-in Matlab) function. For the remainder of this wiki, we assume that the user wants to use a function called funcname in her model.
The External Function
The function can be implemented through a M-file or a MEX file (hereafter, M-/MEX file) located on the MATLAB path. NB: This includes built-in MATLAB functions.
From the mathematical point of view, this function is supposed to be of type 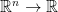 . In other words, it can accept any number of real arguments, but returns only one real argument.
. In other words, it can accept any number of real arguments, but returns only one real argument.
There are two ways in which the user can provide the derivative of funcname to Dynare:
Provide the first (and possibly second) derivatives in the same M-/MEX file as the function itself: The first derivative will be the second return argument (the Jacobian, in a vector) and the second derivative will be the third return argument (the Hessian, in a matrix).
Provide the first (and possibly second) derivatives in separate M-/MEX files: In this case, the only return argument to these functions will be a vector in the case of the Jacobian and a matrix in the case of the Hessian.
Further, the user has the option to provide neither the first nor the second derivative of funcname. In this case (and in the case when the first derivative is provided but the second is not), Dynare will calculate the missing derivatives numerically using finite differences methods (central differences for the Jacobian and eqs. 25.3.24 and 25.3.27 from Abramowitz and Stegun (1965), pg 884 for the Hessian);
Example
1. The case when one M-/MEX file contains the function output, its Jacobian and Hessian:
function [y df d2f]=funcname(a,b) y=a*(b^2); da=b^2; db=2*a*b; df=[da db]; d2f=[0 2*b; 2*b 2*a]; end
2. The case when there is a separate M-/MEX file for funcname and its derivative, funcname_deriv:
function y=funcname(a,b) y=a*(b^2); end function df=funcname_deriv(a,b) da=b^2; db=2*a*b; df=[da db]; end
User Syntax in the .mod file
The keyword external_function is reserved for the declaration of external functions. It accepts the following options:
name = STRING: the name of the function, which must also be the name of the M-/MEX file implementing it.
nargs = INTEGER: the number of arguments of the function. If this option is not provided, Dynare assumes nargs = 1.
first_deriv_provided: tells Dynare that the M-/MEX file specified by the argument passed to name returns the Jacobian as its second output argument.
first_deriv_provided = STRING: tells Dynare that the Jacobian is provided as the only output of the M-/MEX file given as the option argument.
second_deriv_provided: tells Dynare that the M-/MEX file specified by the argument passed to name returns the Hessian as its third output argument.
second_deriv_provided = STRING: tells Dynare that the Hessian is provided as the only output of the M-/MEX file given as the option argument.
The external_function keyword should be used in the first part of the MOD file where the variable declarations are. It should be used once for every external function used.
The user does not need to include an external_function statement if no first or second derivative is provided. In this case, the Dynare preprocessor will recognize the external function (and the number of arguments that have been passed to it) and calculate numerical derivatives as described above.
Examples
1. Declare an external function with name funcname, accepting only one argument, whose derivatives must be computed numerically by Dynare:
external_function(name = funcname);
2. Declare an external function with name funcname, accepting two arguments, whose derivatives are returned as the second and third output arguments of the M-/MEX file funcname:
external_function(name = funcname, nargs = 2, first_deriv_provided, second_deriv_provided);
3. Declare an external function with three arguments, whose first derivative is provided by the M-/MEX file funcname_deriv, and whose second derivative must be computed numerically by Dynare:
external_function(name = funcname, nargs = 3, first_deriv_provided = funcname_deriv);